Overview
Introduction
As technology advances and companies continue to collect and process large amounts of personal data and most data project requires data governance with data security, data privacy within the platform. From a data engineering perspective, how do we comply with those requirements?
Summary: in the article, Author pointed out details of scenarios and use cases with sample implementation on Databricks and follow Lakehouse architecture.
Terminology
PII - Personal Identifiable Information GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation CCPA - California Consumer Privacy Act HIPAA - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act PCI DSS - Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
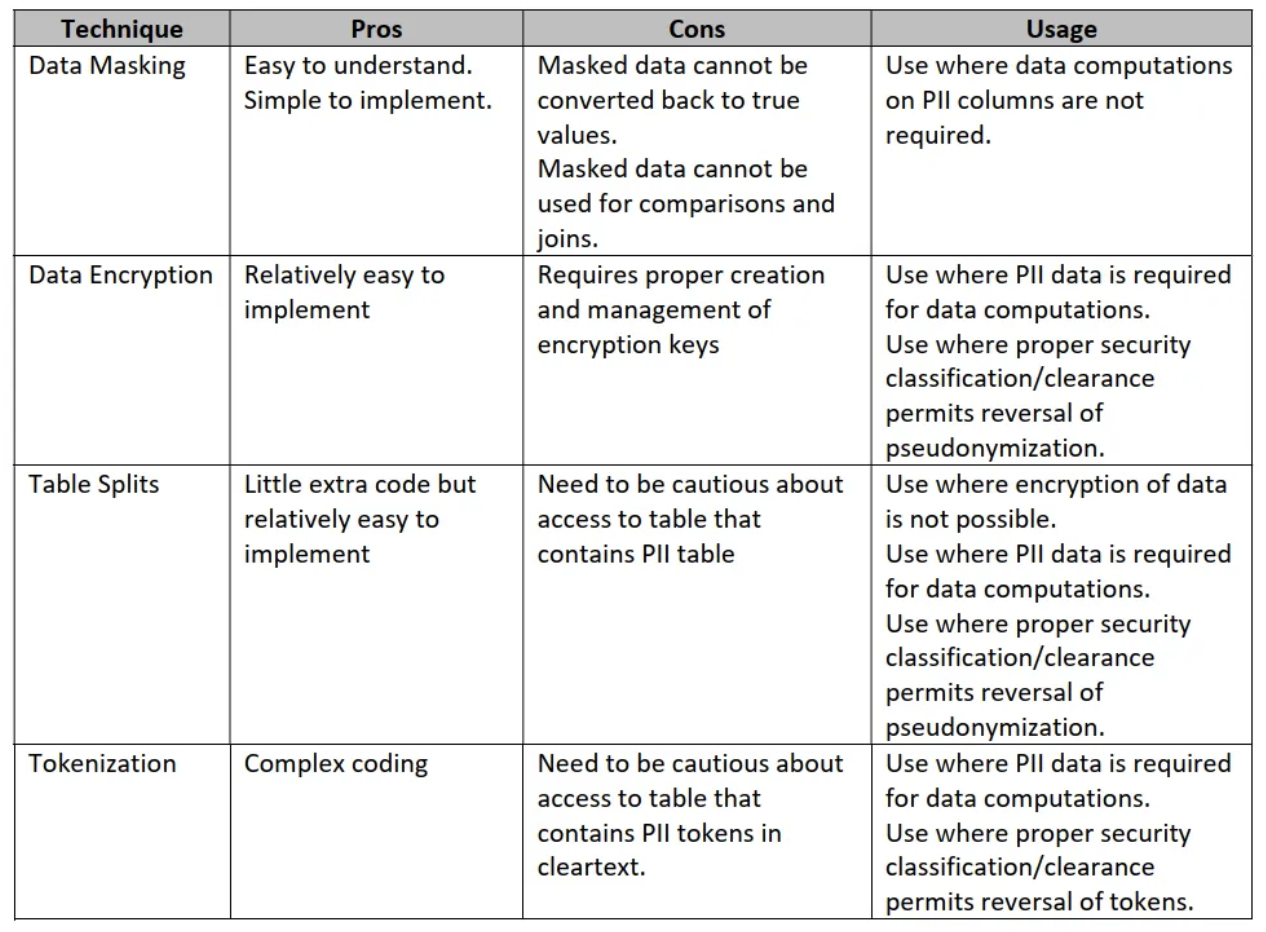
Scenario 1 - Anonymization of PII Data using Data Masking
Using Data Masking is common technique used to protect sensitive data from unauthenticated access. Data Masking involves the process of replacing and converting the sensitive data with “dummy-unvalueable” data to ensure that the original data is not exposed to unauthorized parties.
There are various types of technique that can be used to implement Data Masking:
- Randomization: replacing the original data with randomly generated data
- Substitution: replacing the original data with substitution value that has not relationship with the original data
- Truncation: truncating the original data to shorter length
The implementation is required data privacy policy, programming languages due to it would be implemented within data pipeline.
Scenario 2 - Pseudonymization of PII Data using Data Encryption
Another way of masking data, in Data Encryption technique will replace the original data with pseudonyms, or codes, that do not reveal the original data. This technique involves an algorithm and key to hide data into an unreadable format.
The difference between Masking and Encryption is data is still required for analysis or other purposes at downstream.
The implementation is using Key Management Service (KMS) to encrypt data and only the correct key can be used to decrypt data when consumer is authenticated to read and access the data.
Scenario 3 - Pseudonymization of PII Data by Splitting Tables
By splitting the data into multiple tables using linked keys, only the authored access is possible to read and lookup the real value of the data and mostly this solution is applicable on database/data warehouse.
Splitting table contains PII into PII and Non-PII tables which are linked via KEY, restricted access for PII table.
Important to note that splitting tables does not provide security and full anonymity protection, therefore, it is recommended to use additional technique such masking and encryption to further protect sensitive data.
Scenario 4 - Pseudonymization of PII Data using Tokenization
In case of tokenization, the original data is replaced with unique identifier or token that are generated automatically by tokenization system and the replaced data be able to perform analysis and processing at downstream.
The original data will be securely stored and only returned if consumer is authenticated to read and access the data. Using token for obscuring PII data with token value, lookup the real value by the token.
With tokenization system, it is important to secure with proper designed and implemented to avoid potential security vulnerabilities. Data Engineer should work with Data Architect and Security Engineer to have clear policies and procedures in place for managing and securing both the original data and tokenized data.
